Citation:
Abstract:
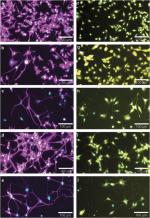
Expanding on a quinazoline scaffold, we developed tricyclic compounds with biological activity. These compounds bind to the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) and protect U118MG (glioblastoma cell line of glial origin) cells from glutamate-induced cell death. Fascinating, they can induce neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells (cell line of pheochromocytoma origin with neuronal characteristics) known to display neuronal characteristics, including outgrowth of neurites, tubulin expression, and NeuN (antigen known as ‘neuronal nuclei’, also known as Rbfox3) expression. As part of the neurodifferentiation process, they can amplify cell death induced by glutamate. Interestingly, the compound 2-phenylquinazolin-4-yl dimethylcarbamate (MGV-1) can induce expansive neurite sprouting on its own and also in synergy with nerve growth factor and with glutamate. Glycine is not required, indicating that N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are not involved in this activity. These diverse effects on cells of glial origin and on cells with neuronal characteristics induced in culture by this one compound, MGV-1, as reported in this article, mimic the diverse events that take place during embryonic development of the brain (maintenance of glial integrity, differentiation of progenitor cells to mature neurons, and weeding out of non-differentiating progenitor cells). Such mechanisms are also important for protective, curative, and restorative processes that occur during and after brain injury and brain disease. Indeed, we found in a rat model of systemic kainic acid injection that MGV-1 can prevent seizures, counteract the process of ongoing brain damage, including edema, and restore behavior defects to normal patterns. Furthermore, in the R6-2 (transgenic mouse model for Huntington disease; Strain name: B6CBA-Tg(HDexon1)62Gpb/3J) transgenic mouse model for Huntington disease, derivatives of MGV-1 can increase lifespan by >20% and reduce incidence of abnormal movements. Also in vitro, these derivatives were more effective than MGV-1.

