Babu, K. N. ; Massarwe, F. ; Reddy, R. R. ; Eghbarieh, N. ; Jakob, M. ; Masarwa*, A. Unsymmetrical 1,1-Bisboryl Species: Valuable Building Blocks in Synthesis.
Molecules 2020,
25, 959.
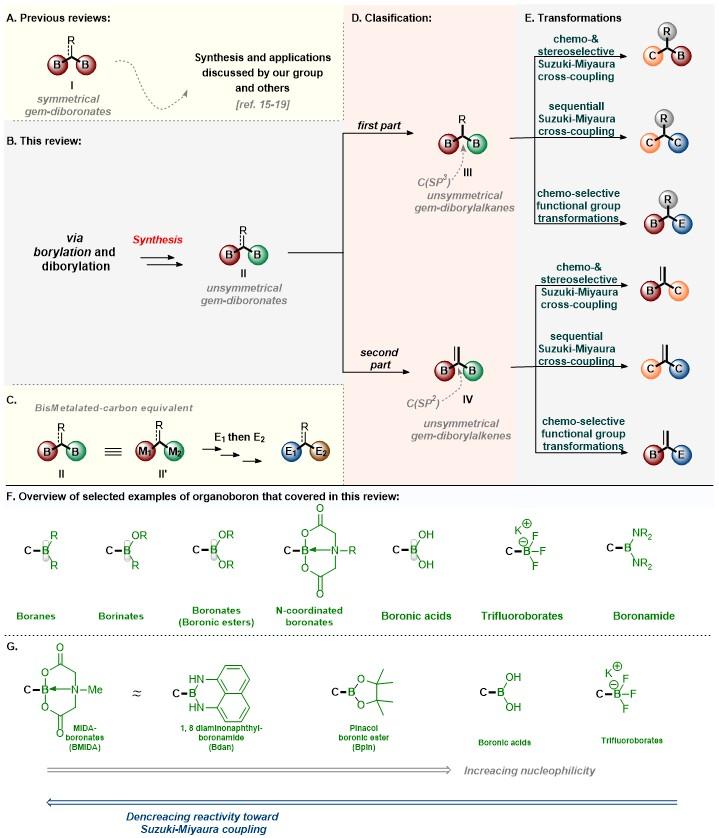
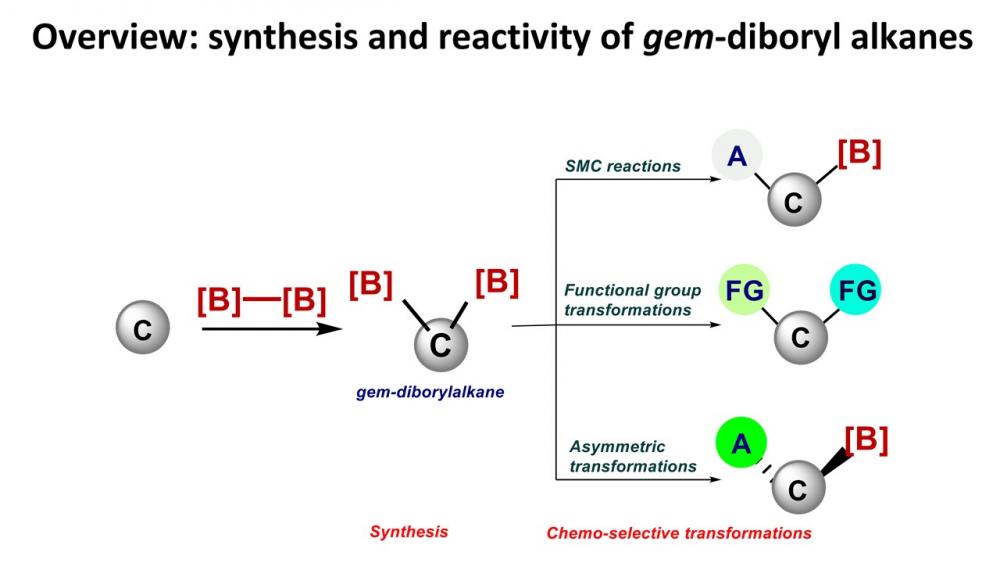
Publisher's VersionAbstractUnsymmetrical 1,1-bis(boryl)alkanes and alkenes are organo-bismetallic equivalents, which are synthetically important because they allow for sequential selective transformations of C–B bonds. We reviewed the synthesis and chemical reactivity of 1,1-bis(boryl)alkanes and alkenes to provide information for the synthetic community. In the first part of this review, we disclose the synthesis and chemical reactivity of unsymmetrical 1,1-bisborylalkanes. In the second part, we describe the synthesis and chemical reactivity of unsymmetrical 1,1-bis(boryl)alkenes.
Kumar, N. ; Eghbarieh, N. ; Stein, T. ; Shames, A. I. ; Masarwa*, A. Photoredox-Mediated Reaction of gem-Diborylalkenes: ReactivityToward Diverse 1,1-Bisborylalkanes.
Chemistry—A European Journal 2020,
26, 5360.
Publisher's VersionAbstractThe use of gem-diborylalkenes as light-reactive groups is explored for the first time. These reactions provide an efficient and general method for the photochemical conversion of gem-diborylalkenes to rapidly access 1,1-bisborylalkanes. This method exploits a novel photoredox decarboxylative radical addition to gem-diborylalkenes to afford α-gemdiboryl carbon-centered radicals, which benefit from additional stability by virtue of an interaction with the empty p-orbitals on borons. The reaction offers a highly modular and regioselective approach to γ-amino gem-diborylalkanes. Furthermore, EPR spectroscopy and DFT calculations have provided insight into the radical mechanism underlying the photochemistry reaction.
Kumar, N. ; Reddy, R. R. ; Eghbarieh, N. ; Masarwa*, A. α-Borylalkyl Radicals: Their Distinctive Reactivity in Modern Organic Synthesis.
Chemical Communications 2020, 13-25.
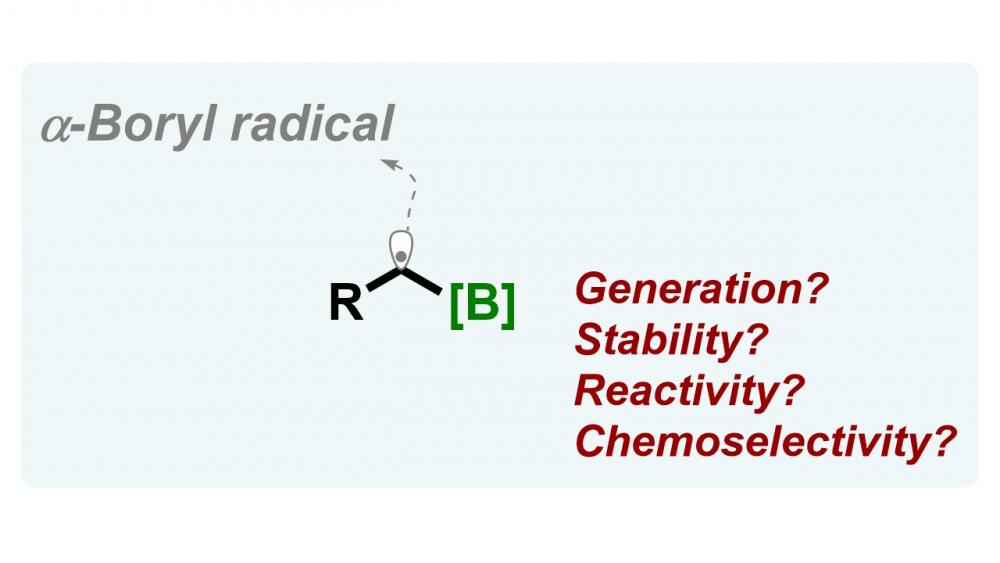
Publisher's VersionAbstractOrganoborons are extremely important for synthetic organic chemistry; they can serve as advanced intermediates for a variety of transformations. Such a well-known transformation involves the loss of the boron moiety, creating alkyl radicals. Although these originally developed protocols for alkyl radical generation remain in active use today, in recent years their α-boryl carbon-centred radicles have been joined by a new array of radical generation strategies that offer a unique reactivity to forge a wider diversity of organoborones that often operate under mild and benign conditions. Herein, we will highlight the stability and reactivity of α-borylalkyl radicals and their remarkably recent advances in order to further utilise them for C–C and C–heteroatom bond formation. Their use for this purpose has been reported over the last decade in an attempt to guide the synthetic community. Various transition-metal and metal-free methods for their generation are presented, and more advanced photoredox approaches are discussed, mainly for the period of time 2009-2019.
rajender nallagonda, ; Kumar, N. ; Reddy, R. R. ; Shioukhi, I. ; Sagih, H. ; Masarwa*, A. Synthesis and Reactivity of 1,1 and 1,2-Bisboronate Species.
(PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups) John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, England 2020.
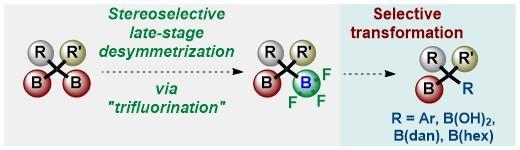
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn the past four decades, the chemistry of 1,1‐ and 1,2‐bisboronate compounds has been extensively explored. Many interesting structural features and reaction patterns have emerged, and more importantly, these compounds now feature prominently in both metal‐catalyzed and metal‐free transformations for the formation of CC bonds and C–heteroatom and other processes. This chapter aims to highlight the recent development in this rising research field, focusing on the synthesis of 1,1‐ and 1,2‐bisboronate compounds and their reactivity and selectivity that originate from the use of these bisboronates.