Citation:

Abstract:
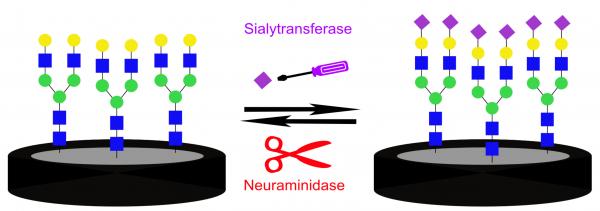
Sialylated glycans and glycoproteins are involved in cellular communication and are crucial for distinguishing between signal pathways. Sialylation levels and patterns modulate recognition events and are regulated by the enzymatic activity of sialyltransferases and neuraminidases. Abnormal activity of these enzymes is related to diseases such as cancer and viral infection. Monitoring these enzymatic activities offers valuable diagnostic tools. This work presents an impedimetric biosensing platform for following and detecting sialylation and desialylation processes. This platform is based on a native biantennary N-glycan substrate attached to a glassy carbon electrode. Changes in the molecular layer, as a result of enzymatic reactions, were detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, displaying high sensitivity to the enzymatic surface reactions. Increase in the molecular layer roughness in response to the sialylation was visualized using atomic force microscopy. After enzymatic sialylation, the presence of sialic acid was confirmed using cyclic voltammetry by coupling of the redox active marker aminoferrocene. The sialylation showed selectivity toward the N-glycan compared to another glycan substrate. A time dependent sialylation was followed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, proving that the new system can be applied to evaluate the enzymatic kinetics. Our findings suggest that analyzing sialylation processes using this platform can become a useful tool for the detection of pathological states and pathogen invasion.