Citation:
Abstract:
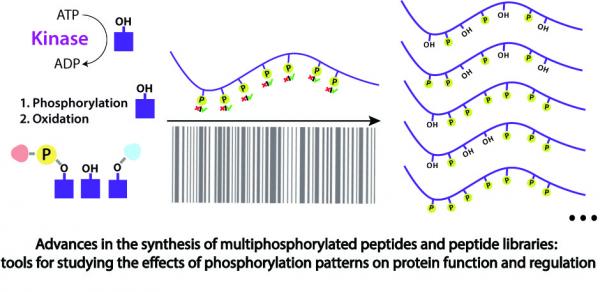
Unraveling the role of post-translational modification (PTM) patterns is one of the most urgent and unresolved issues facing the scientific community. Attempts to crack the phosphorylation bio-barcode led to significant findings, which suggest that many proteins cannot be regarded as a single entity but exist as several forms which differ in their phosphorylation patterns and their functions. While protein regions that do not contain PTMs can be rather simply mimicked using peptide libraries, heavily phosphorylated regions are much harder to study using the same tools. The differences between the syntheses of simple mono-, di- and tri-phosphopeptides and the synthesis of multiphosphopeptides are dramatic. While simple phosphopeptides can be synthesized using almost standard SPPS strategies, the synthesis of multiphosphopeptides is to date a major synthetic challenge. Synthesis of multiphosphopeptides requires the insertion of several phosphate groups simultaneously or sequentially into various positions on the peptide in the presence of many other potential modification sites. These groups are bulky, unstable and cannot be easily introduced when in close proximity. Moreover, since the same protein region can possess many alternative multiphosphorylation patterns, libraries comprising a large number of peptides with different degrees and positions of phosphorylation are essential. Many strategies have been developed to provide routes to enable the preparation of multiphosphopeptides. These methods are essentially different from the methods used for the preparation of simple phosphopeptides. In this review, we specifically emphasize the challenges and importance of synthesizing multiphosphopeptides and their libraries. The historical perspective and state of the art strategies are described. We demonstrate here how the different synthetic approaches attempt to address the special problems associated with the synthesis of multiphosphopeptides. The advantages and disadvantages of each strategy are discussed in order to provide a roadmap for the synthesis of such libraries. An overview of the existing strategies and some comments regarding future directions are provided. Applications of multiphosphopeptide libraries as tools to study the effect of phosphorylation patterns on the biological function of proteins are also described.