Citation:
Date Published:
OCT 18Abstract:
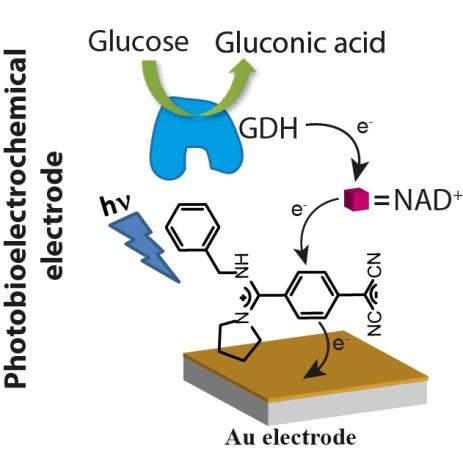
A 7-pyrrolidino-7-benzylamino-8,8-dicyanoquinodimethane, PBEDQ, (1), donor-acceptor-modified electrode yields, in the presence of hydroquinone, (2), an anodic photocurrent with quantum efficiency of 1.5%. The PBEDQ-functionalized electrode yields, in the presence of the electron acceptor diquat, (3), a cathodic photocurrent with a quantum efficiency corresponding to 2.1%. The electron transfer cascades leading to the anodic or cathodic photo currents in the different systems are discussed. It is further demonstrated that the integration of 1,4-dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, as electron donor, with the PBEDQ-modified electrode leads to an anodic photocurrent. This allowed the assembly of a photobioelectrochemical integrated electrode composed of the photoactive PBEDQ donor-acceptor compound, NAD(+) as cofactor, and the NAD(+)-dependent glucose dehydrogenase, GDH. Irradiation of the integrated electrode in the presence of glucose results in the GDH-biocatalyzed oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid with the concomitant generation of NADH that acts as electron donor for the photo active donor-acceptor PBEDQ units, leading to the generation of steady-state anodic photocurrent. The photocurrent intensities are controlled by the concentrations of glucose. The integrated PBEDQ/NAD(+)/GDH electrodes introduces a functional photobioelectrochemical electrode for the detection of glucose, and demonstrates the assembly of a functional photo-biofuel cell that uses light and a biomass product (glucose) for the generation of electric power.