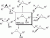
Vainshtein, A. ; Veenman, L. ; Shterenberg, A. ; Singh, S. ; Masarwa, A. ; Dutta, B. ; Island, B. ; Tsoglin, E. ; Levin, E. ; Leschiner, S. ; et al. Quinazoline-Based Tricyclic Compounds that Regulate Programmed Cell Death, Induce Neuronal Differentiation, and are Curative in Animal Models for Excitotoxicity and Hereditary Brain Disease.
Cell Death Discovery 2015,
1 15027.
Publisher's VersionAbstractExpanding on a quinazoline scaffold, we developed tricyclic compounds with biological activity. These compounds bind to the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) and protect U118MG (glioblastoma cell line of glial origin) cells from glutamate-induced cell death. Fascinating, they can induce neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells (cell line of pheochromocytoma origin with neuronal characteristics) known to display neuronal characteristics, including outgrowth of neurites, tubulin expression, and NeuN (antigen known as ‘neuronal nuclei’, also known as Rbfox3) expression. As part of the neurodifferentiation process, they can amplify cell death induced by glutamate. Interestingly, the compound 2-phenylquinazolin-4-yl dimethylcarbamate (MGV-1) can induce expansive neurite sprouting on its own and also in synergy with nerve growth factor and with glutamate. Glycine is not required, indicating that N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are not involved in this activity. These diverse effects on cells of glial origin and on cells with neuronal characteristics induced in culture by this one compound, MGV-1, as reported in this article, mimic the diverse events that take place during embryonic development of the brain (maintenance of glial integrity, differentiation of progenitor cells to mature neurons, and weeding out of non-differentiating progenitor cells). Such mechanisms are also important for protective, curative, and restorative processes that occur during and after brain injury and brain disease. Indeed, we found in a rat model of systemic kainic acid injection that MGV-1 can prevent seizures, counteract the process of ongoing brain damage, including edema, and restore behavior defects to normal patterns. Furthermore, in the R6-2 (transgenic mouse model for Huntington disease; Strain name: B6CBA-Tg(HDexon1)62Gpb/3J) transgenic mouse model for Huntington disease, derivatives of MGV-1 can increase lifespan by >20% and reduce incidence of abnormal movements. Also in vitro, these derivatives were more effective than MGV-1.
Marek*, I. ; Masarwa, A. ; Delaye, P. - O. ; Leibeling, M. Selective Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage for the Stereoselective Synthesis of Acyclic Systems.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
54, 414-429.
Publisher's VersionAbstractMost of the efforts of organic chemists have been directed to the development of creative strategies to build carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bonds in a predictable and efficient manner. In this Review, we show an alternative approach where challenging molecular skeletons could be prepared through selective cleavage of carbon–carbon bonds. We demonstrate that it has the potential to be a general principle in organic synthesis for the regio-, diastereo-, and even enantioselective preparation of adducts despite the fact that C![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) C single bonds are among the least reactive functional groups. The development of such strategies may have an impact on synthesis design and can ultimately lead to new selective and efficient processes for the utilization of simple hydrocarbons.
C single bonds are among the least reactive functional groups. The development of such strategies may have an impact on synthesis design and can ultimately lead to new selective and efficient processes for the utilization of simple hydrocarbons.
Masarwa, A. ; Gerbig, D. ; Oskar, L. ; Loewenstein, A. ; Reisenauer, H. P. ; Lesot*, P. ; Schreiner*, P. R. ; Marek*, I. Synthesis and Stereochemical Assignment of Crypto-Optically Active 2H6-Neopentane.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
54, 13106–13109.
Publisher's VersionAbstractThe determination of the absolute configuration of chiral molecules is at the heart of asymmetric synthesis. Here we probe the spectroscopic limits for chiral discrimination with NMR spectroscopy in chiral aligned media and with vibrational circular dichroism spectroscopy of the sixfold-deuterated chiral neopentane. The study of this compound presents formidable challenges since its stereogenicity is only due to small mass differences. For this purpose, we selectively prepared both enantiomers of 2H6-1 through a concise synthesis utilizing multifunctional intermediates. While NMR spectroscopy in chiral aligned media could be used to characterize the precursors to 2H6-1, the final assignment could only be accomplished with VCD spectroscopy, despite the fleetingly small dichroic properties of 1. Both enantiomers were assigned by matching the VCD spectra with those computed with density functional theory.
Weber, M. ; Owens, K. ; Masarwa*, A. ; Sarpong*, R. Construction of Enantiopure Taxoid and Natural Products-Like Scaffolds Using a C-C Bond Cleavage/Arylation Reaction.
Org. Lett. 2015,
17, 5432–5435.
Publisher's VersionAbstractAn approach to construct enantiopure complex natural product-like frameworks, including the first reported synthesis of a C17 oxygenated taxoid scaffold, is presented. A palladium-catalyzed C–C activation/cross-coupling is utilized to access these structures in a short sequence from (+)-carvone; the scope of this reaction is explored.
Masarwa, A. ; Weber, M. ; Sarpong*, R. Selective C-C and C-H bond Activation/Cleavage of Pinene Derivatives: Synthesis Of Enantiopure Cyclohexanone Scaffolds and Mechanistic insights.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015,
137, 6327-6334.
Publisher's VersionAbstractThe continued development of transition-metal-mediated C−C bond activation/cleavage methods would provide even more opportunities to implement novel synthetic strategies. We have explored the Rh(I)-catalyzed C−C activation of cyclobutanols resident in hydroxylated derivatives of pinene, which proceed in a complementary manner to the C−C bond cleavage that we have observed with many traditional electrophilic reagents. Mechanistic and computational studies have provided insight into the role of C−H bond activation in the stereochemical outcome of the Rh-catalyzed C−C bond activation process. Using this new approach, functionalized cyclohexenones that form the cores of natural products, including the spiroindicumides and phomactin A, have been accessed.






![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) C single bonds are among the least reactive functional groups. The development of such strategies may have an impact on synthesis design and can ultimately lead to new selective and efficient processes for the utilization of simple hydrocarbons.
C single bonds are among the least reactive functional groups. The development of such strategies may have an impact on synthesis design and can ultimately lead to new selective and efficient processes for the utilization of simple hydrocarbons.