Citation:
| dou2019stochastic.pdf | 1.08 MB |
Abstract:
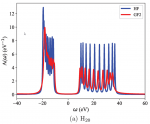
We develop a stochastic resolution of identity approach to the real-time second-order Green’s function (real-time sRI-GF2) theory, extending our recent work for imaginary-time Matsubara Green’s function [Takeshita et al. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 044114]. The approach provides a framework to obtain the quasi-particle spectra across a wide range of frequencies and predicts ionization potentials and electron affinities. To assess the accuracy of the real-time sRI-GF2, we study a series of molecules and compare our results to experiments as well as to a many-body perturbation approach based on the GW approximation, where we find that the real-time sRI-GF2 is as accurate as self-consistent GW. The stochastic formulation reduces the formal computatinal scaling from O(Ne5) down to O(Ne3) where Ne is the number of electrons. This is illustrated for a chain of hydrogen dimers, where we observe a slightly lower than cubic scaling for systems containing up to Ne ≈ 1000 electrons.